

Using '-help‘ switch will display a list of available option that is used with df command. For example, the following command will only display other file systems types other than ext3. If you want to display a file system type that doesn’t belongs to the ext3 type use the option ‘ -x‘. For example, the following command will only display the ext3 file system. If you want to display a certain file system type use the ‘ -t‘ option. ~]# df -Tįilesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on It will display file system type along with other information. To check the file system type of your system use the option ‘ T‘. If you notice all the above commands output, you will see there is no Linux file system type mentioned in the results. ~]# df -iįilesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on Using ‘ -i‘ switch will display the information of a number of used inodes and their percentage for the file system. To display information of all file system statistics in GB ( Gigabyte) use the option as ‘ df -h‘. ~]# df -mįilesystem 1M-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on To display information of all file system usage in MB ( MegaByte) use the option ‘ -m‘. To display all file system information and usage in 1024-byte blocks, use the option ‘ -k‘ (e.g. Display Information of File System in Bytes ~]# df -hT /homeįilesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
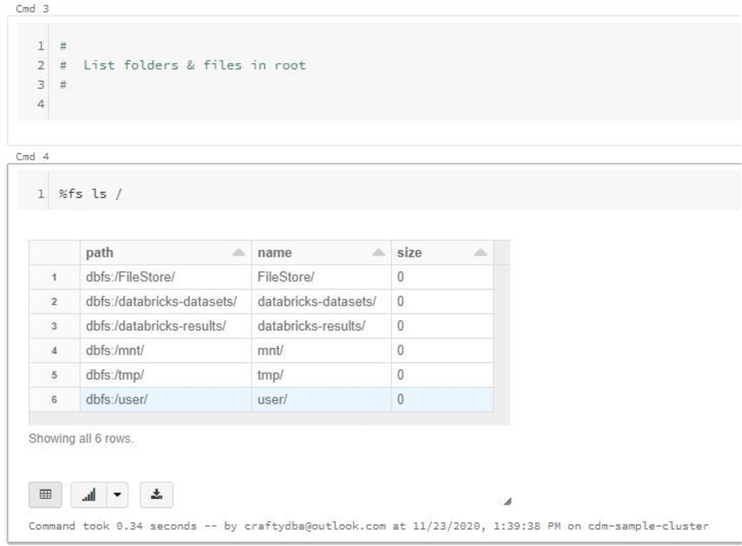

To see the information of only device /home file systems in human-readable format use the following command. ~]# df -hįilesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on The df command provides an option to display sizes in Human Readable formats by using '-h' (prints the results in human-readable format (e.g., 1K 2M 3G)). as it makes it very easy to understand and remember. Have you noticed that the above commands display information in bytes, which is not readable at all because we are in a habit of reading the sizes in megabytes, gigabytes, etc. Show Disk Space Usage in Human Readable Format Sunrpc 0 0 0 - /var/lib/nfs/rpc_pipefs 3. The same as above, but it also displays information of dummy file systems along with all the file system disk usage and their memory utilization. Display Information of all File System Disk Space Usage ~]# dfįilesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on The “ df” command displays the information of device name, total blocks, total disk space, used disk space, available disk space, and mount points on a file system. So, you could better understand the usage of the df command in Linux.
#Finding df root folder full#
This article explains a way to get the full information of Linux disk space usage with the help of the ‘ df‘ command with their practical examples. Using ‘ -h‘ parameter with ( df -h) will show the file system disk space statistics in “ human-readable” format, means it gives the details in bytes, megabytes, and gigabyte. The ‘ df‘ command stands for “ disk filesystem“, it is used to get a full summary of available and used disk space usage of the file system on the Linux system. However, Linux has a strong built-in utility called ‘ df‘. On the internet, you will find plenty of tools for checking disk space utilization in Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
